PCOS is a common hormonal disorder affecting people with ovaries, characterized by:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Excess androgen (male hormones) → acne, hirsutism (excess hair growth)
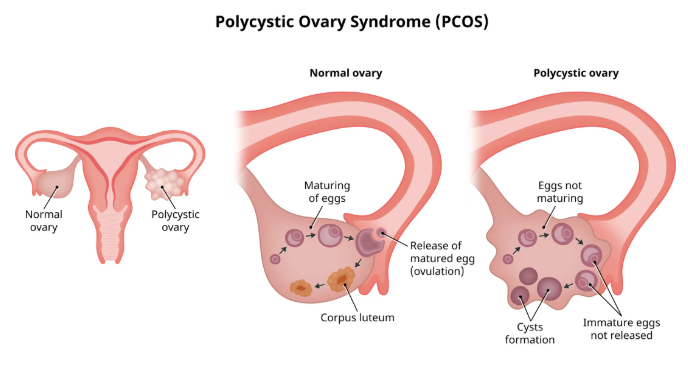
- Polycystic ovaries (multiple small follicles on ultrasound)
It is a leading cause of infertility and increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Contents
- Causes
- Risk Factors
- Symptoms
- 1. Menstrual Irregularities
- 2. Androgen Excess (Hyperandrogenism)
- 3. Metabolic Symptoms
- 4. Ovarian Cysts (Not Always Present!)
- Types of PCOS
- Diagnosis (Rotterdam Criteria)
- Tests Performed:
- Treatment (Depends on Goals)
- 1. Lifestyle Changes (First-Line Treatment)
- 2. Medications
- For Hormonal Regulation
- For Fertility
- For Hair/Skin Symptoms
- Complications
- Prevention
- Prognosis
Causes
The exact cause is unknown, but key factors include:
- Insulin Resistance (70% of cases) → High insulin → ↑ androgens
- Hormonal Imbalance → High LH (luteinizing hormone), low FSH → ↑ testosterone
- Genetics (runs in families)
- Chronic Inflammation → Linked to insulin resistance
- Environmental Factors (obesity, endocrine disruptors)
Risk Factors
- Family history of PCOS or diabetes
- Obesity (worsens insulin resistance)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Insulin resistance or prediabetes
Symptoms
Symptoms vary but commonly include:
1. Menstrual Irregularities
- Infrequent, heavy, or absent periods
- Difficulty ovulating → infertility
2. Androgen Excess (Hyperandrogenism)
- Hirsutism (facial/body hair)
- Acne, oily skin
- Male-pattern baldness
3. Metabolic Symptoms
- Weight gain (especially abdominal)
- Dark skin patches (acanthosis nigricans)
- Prediabetes/diabetes
4. Ovarian Cysts (Not Always Present!)
- “String of pearls” appearance on ultrasound
Types of PCOS
PCOS is classified based on hormonal and metabolic profiles:
- Insulin-Resistant PCOS (Most common)
- High insulin → ↑ androgens
- Weight gain, prediabetes
- Post-Pill PCOS
- Temporary PCOS-like symptoms after stopping birth control
- Inflammatory PCOS
- Chronic inflammation → hormone disruption
- Fatigue, headaches, joint pain
- Adrenal PCOS (Rare)
- High DHEA-S (adrenal androgen) but normal ovarian androgens
Diagnosis (Rotterdam Criteria)
Diagnosis requires 2 out of 3:
- Irregular/absent periods
- Hyperandrogenism (clinical or lab-confirmed)
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound
Tests Performed:
- Blood tests: LH, FSH, testosterone, DHEA-S, AMH, insulin, glucose
- Pelvic ultrasound (to check ovarian cysts)
- Glucose tolerance test (for insulin resistance)
Treatment (Depends on Goals)
1. Lifestyle Changes (First-Line Treatment)
- Weight loss (5-10% improves symptoms significantly)
- Low-glycemic diet (whole grains, lean protein, healthy fats)
- Exercise (30+ mins daily, mix cardio + strength training)
2. Medications
For Hormonal Regulation
- Birth control pills (regulate periods, reduce androgens)
- Metformin (improves insulin resistance)
- Anti-androgens (spironolactone, flutamide) → reduce acne/hair growth
For Fertility
- Clomiphene (Clomid) or Letrozole (induce ovulation)
- IVF (if other treatments fail)
For Hair/Skin Symptoms
- Topical retinoids (acne)
- Laser hair removal (hirsutism)
Complications
- Infertility (from lack of ovulation)
- Type 2 diabetes (50% risk by age 40)
- Cardiovascular disease (high cholesterol, hypertension)
- Endometrial cancer (from unopposed estrogen)
- Depression/anxiety (due to hormonal and body image issues)
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Balanced diet (low sugar, high fiber)
- Early diagnosis & management
Prognosis
- No cure, but manageable with lifestyle + meds
- Fertility often improves with treatment
- Long-term metabolic risks require monitoring