Contents
1. Etiology
- Pathogen: Hepatitis C virus (HCV), Flaviviridae family.
- Genotypes: 6 major types; 1b dominates in Russia (more aggressive).
- Features:
- High mutation rate (evades immunity).
- 80% become chronic.
2. Transmission
- Bloodborne (main route):
- IV drug use (shared needles).
- Unsterile tools (tattoos, piercings).
- Blood transfusions (pre-1992).
- Sexual (rare, requires blood contact).
- Vertical (mother to child during birth, 5% risk).
Not transmitted:
- Via hugs, kissing, sharing food.
- Through breast milk (unless cracked nipples).
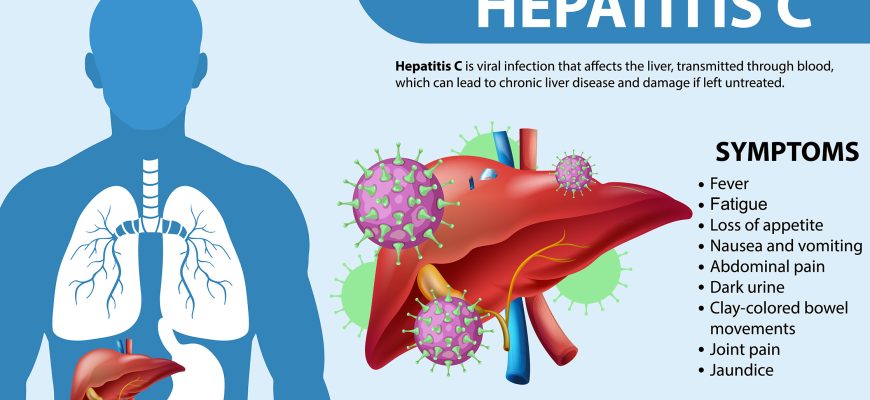
3. Symptoms
Acute phase (first 6 months):
- 80% asymptomatic.
- Rarely: fatigue, nausea, jaundice (20%).
Chronic form:
- Fatigue, depression.
- Abdominal discomfort, itchy skin.
- Late stages: cirrhosis, ascites, liver failure.
4. Diagnosis
- Anti-HCV antibodies (screening, doesn’t differentiate acute/chronic).
- HCV RNA PCR (confirms active infection).
- Genotyping (guides treatment).
- FibroTest/elastography (liver fibrosis assessment).
Key point:
- Post-exposure testing: 2–4 weeks (PCR), 3–6 months (antibodies).
5. Prevention
- Avoid blood contact.
- Personal hygiene items (razors, nail clippers).
- Condoms with HCV-positive partners.
- No vaccine, but cure exists.
6. Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs):
- Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (12 weeks, 98% cure).
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (8–12 weeks).
Cure criteria:
- Sustained virologic response (SVR) — undetectable HCV RNA 12 weeks post-treatment.
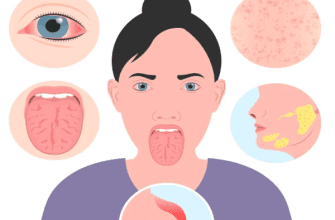
7. How to Recognize?
Red flags:
- Unexplained chronic fatigue.
- Yellow skin/eyes (jaundice).
- Spider angiomas (“liver stars”).
- Abdominal swelling (ascites).
8. Post-Exposure Protocol
- Blood on skin: Wash with soap → apply 70% alcohol.
- Needlestick: Squeeze blood out → rinse → emergency prophylaxis (prescribed by doctor).
- At 2 weeks: HCV RNA PCR.
- At 3 months: Anti-HCV + PCR.
9. How to Identify HCV in Others?
Clues:
- Constant exhaustion.
- Jaundice.
- Red palmar erythema.
But:
- 80% of carriers are unaware until late stages!
- Only lab tests confirm infection.