What Is Astigmatism?
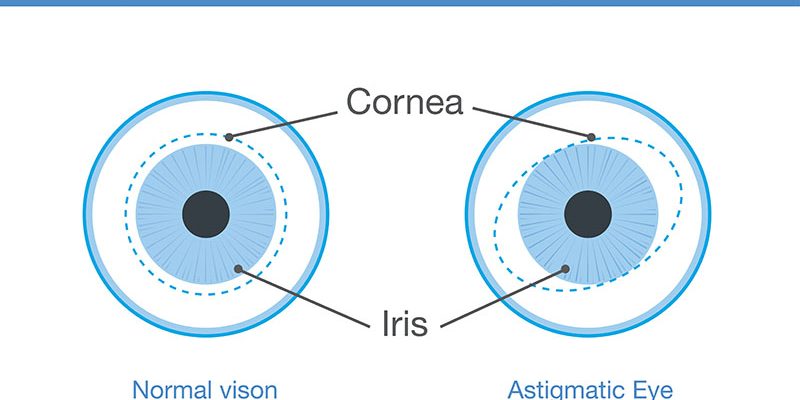
Astigmatism is a common refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision at all distances. It often occurs alongside nearsightedness (myopia) or farsightedness (hyperopia).
Key Facts (American Academy of Ophthalmology [AAO]):
✔ Affects 1 in 3 Americans to some degree
✔ Usually present at birth but can develop later
✔ Not a disease—simply a focusing imperfection
✔ Easily corrected with glasses, contacts, or surgery
Types of Astigmatism (AAO & NIH)
- Corneal Astigmatism (Most Common)
- Caused by an irregularly curved cornea (like a football instead of a basketball).
- Lenticular Astigmatism
- Due to an unevenly shaped lens inside the eye.
- Regular vs. Irregular Astigmatism
- Regular: Cornea has symmetrical curvature (correctable with standard lenses).
- Irregular: Cornea is uneven (often due to injury or keratoconus; may require special contacts).
Symptoms (Mayo Clinic)
✔ Blurred or distorted vision (near and far)
✔ Eye strain or discomfort (especially after reading/screens)
✔ Headaches (from squinting to focus)
✔ Difficulty seeing at night (glare/halos around lights)
✔ Frequent squinting
Not Typically Present: Eye pain or sudden vision loss (may indicate other issues).
Diagnosis (American Optometric Association [AOA])
- Comprehensive Eye Exam – Includes:
- Visual acuity test (Snellen chart).
- Keratometry (measures corneal curvature).
- Refraction test (determines lens prescription).
- Corneal topography (for irregular astigmatism).
Treatment (AAO & FDA)
- Corrective Lenses (Most Common)
- Glasses: Cylindrical lenses compensate for the irregular curvature.
- Torric Contact Lenses: Soft or rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses.
- Refractive Surgery (For Adults)
- LASIK/PRK: Reshapes the cornea.
- Toric IOLs: Implanted during cataract surgery.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K)
- Special overnight contacts that temporarily reshape the cornea.
Prevention (CDC & AAO)
✅ Regular eye exams (every 1-2 years, especially for kids).
✅ Protect eyes from injury (safety goggles for sports/work).
✅ Manage screen time (follow the 20-20-20 rule).
✅ No proven way to prevent astigmatism, but early correction prevents strain.
Red Flags: When to See a Doctor (AAO)
Seek immediate care if:
- Sudden vision changes (could indicate keratoconus or other conditions).
- Eye pain or redness (may signal infection or injury).
- Double vision (new onset could indicate neurological issues).
Schedule an exam if:
- Blurred vision affects daily tasks (driving, reading).
- Headaches or eye fatigue persist.