About Health
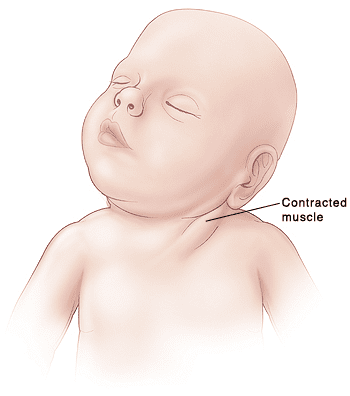
Muscular Torticollis: A Comprehensive Guide What It Is Muscular torticollis, also known as congenital muscular torticollis (CMT) when present in infants
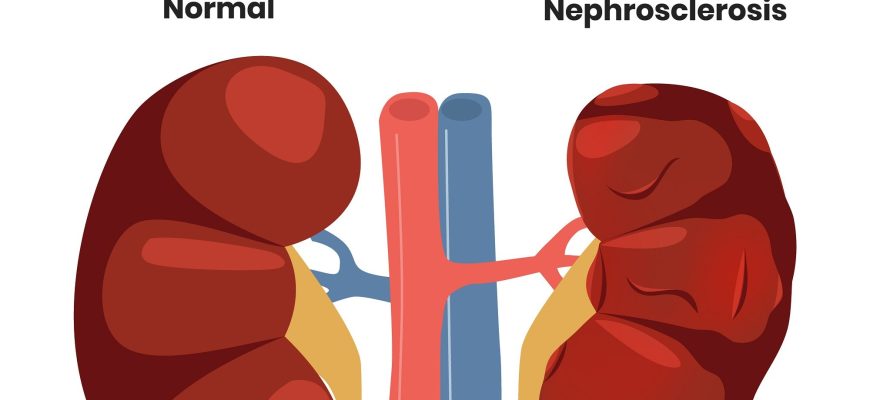
What Is Kidney Failure? Kidney failure (renal failure) occurs when the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluids
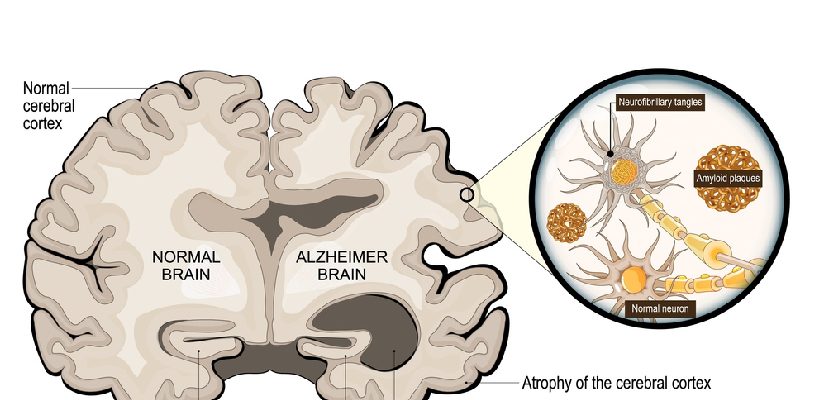
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease? Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the most common cause of dementia
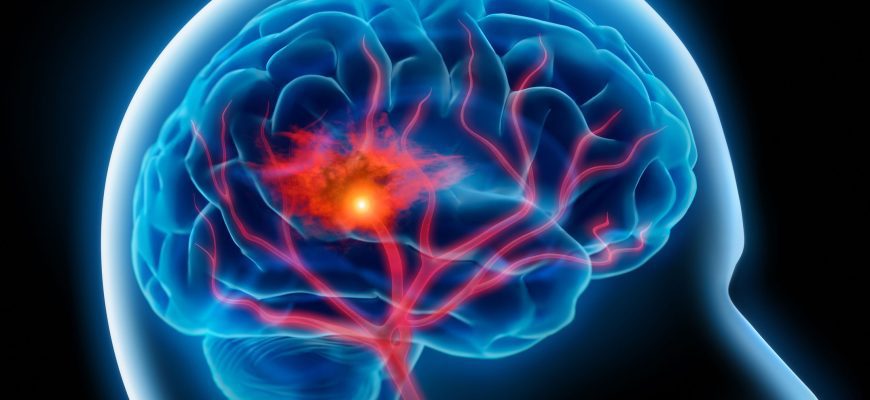
What Is a Stroke? A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die within minutes. It’s a
What Is Dementia? Dementia is a progressive decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life. It is caused by
What Is Parkinson’s Disease? Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons
What Is Epilepsy? Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures caused by abnormal electrical
What Is Amblyopia? Amblyopia is a vision development disorder where one eye fails to achieve normal visual acuity, even with glasses or contacts.
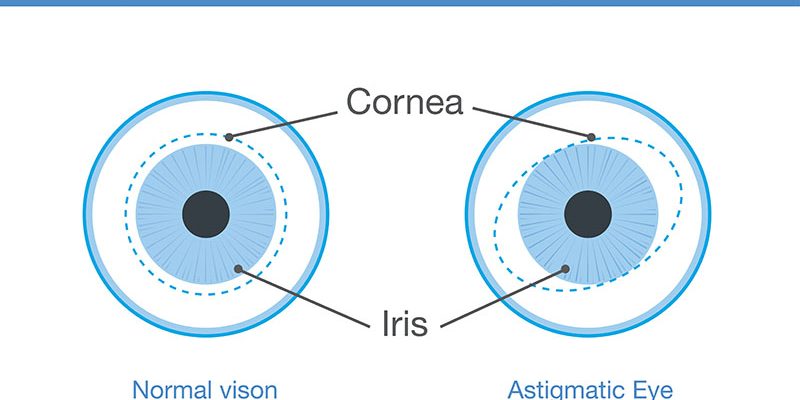
What Is Astigmatism? Astigmatism is a common refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to
What Is Blepharitis? Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids, typically affecting the eyelash follicles or