About Health
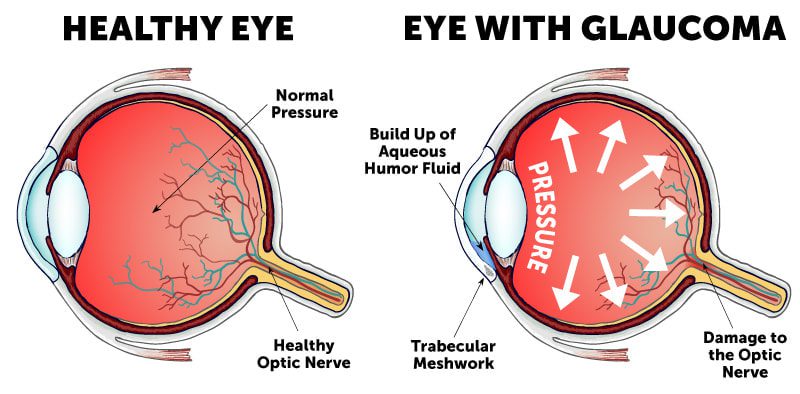
What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, typically caused by high intraocular pressure (IOP). It’
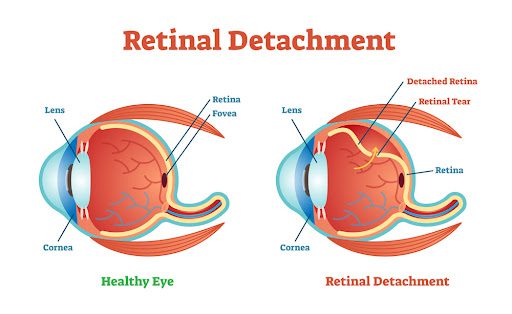
What Is Retinal Detachment? Retinal detachment occurs when the retina (the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye)
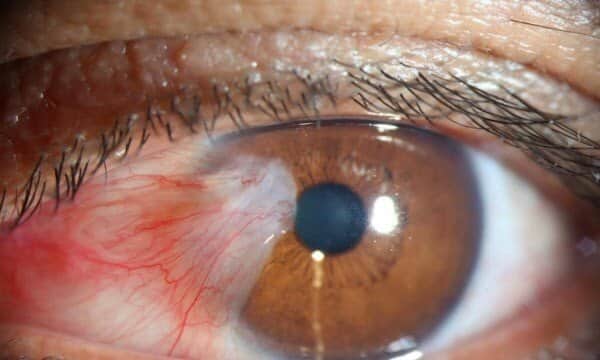
What is a Pterygium? A pterygium is a non-cancerous growth of pink, fleshy tissue on the eye’s conjunctiva that extends onto the cornea.
About Health
What is Electroophthalmia? Electroophthalmia (commonly called photokeratitis or UV keratitis) is a painful eye condition
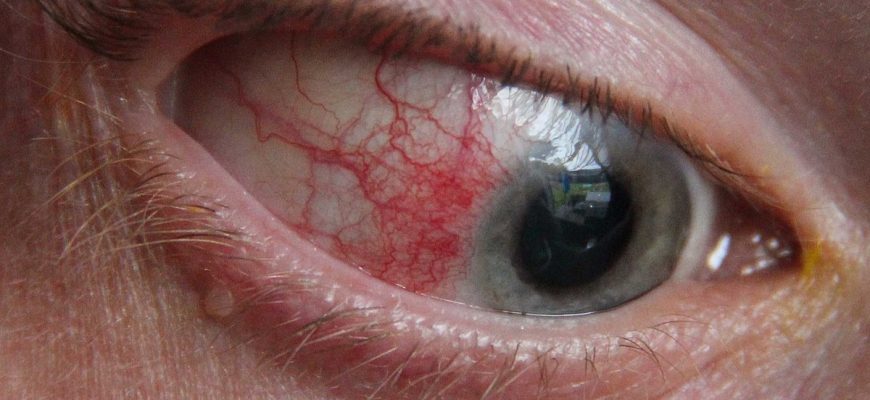
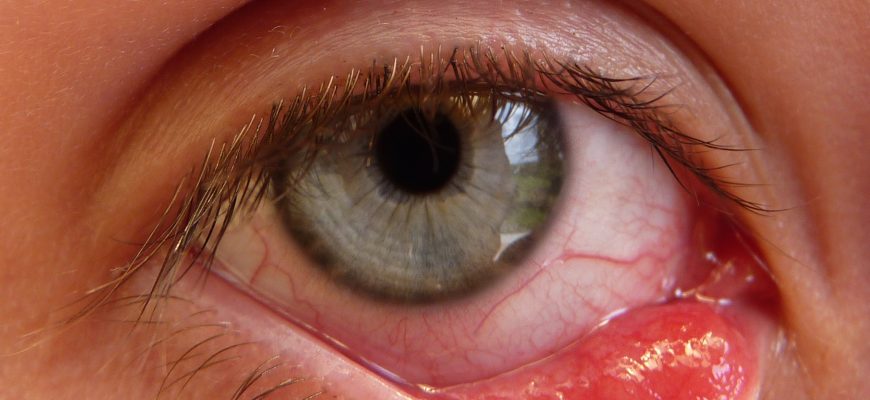
What Is Episcleritis? Episcleritis is inflammation of the episclera, the thin vascular layer between the white of the eye (sclera) and the clear conjunctiva.
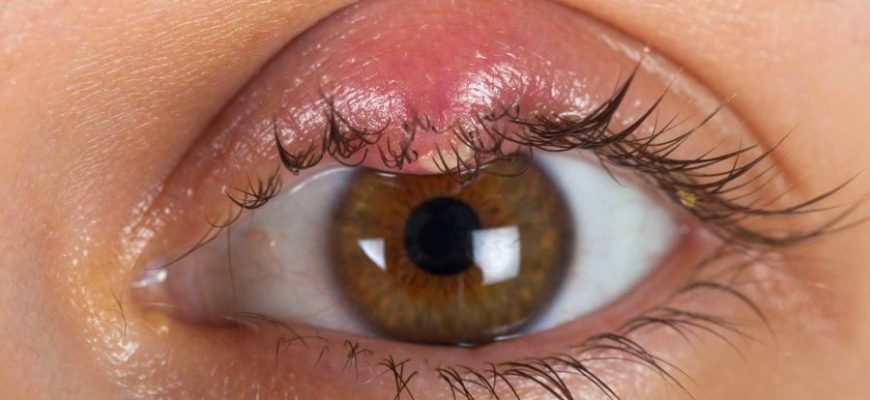
What is a Stye? A stye (hordeolum) is a painful red bump near the edge of the eyelid caused by bacterial infection of oil glands
What Is a Chalazion? A chalazion is a painless, slow-growing lump on the eyelid caused by a blocked oil gland (meibomian gland).
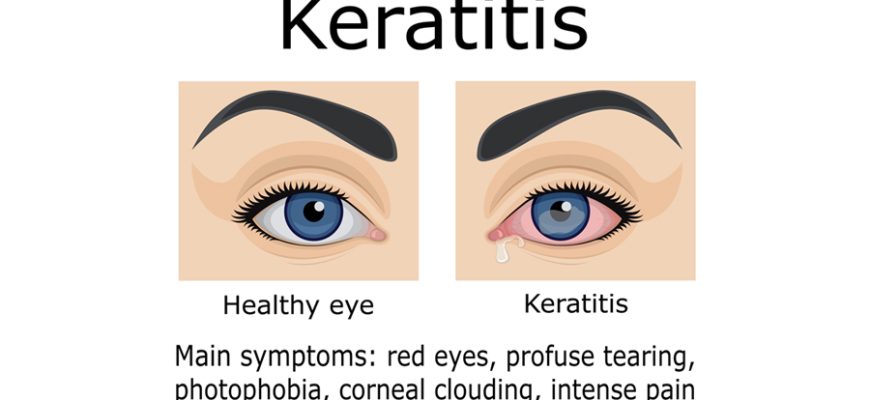
What Is Keratitis? Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). It can be infectious
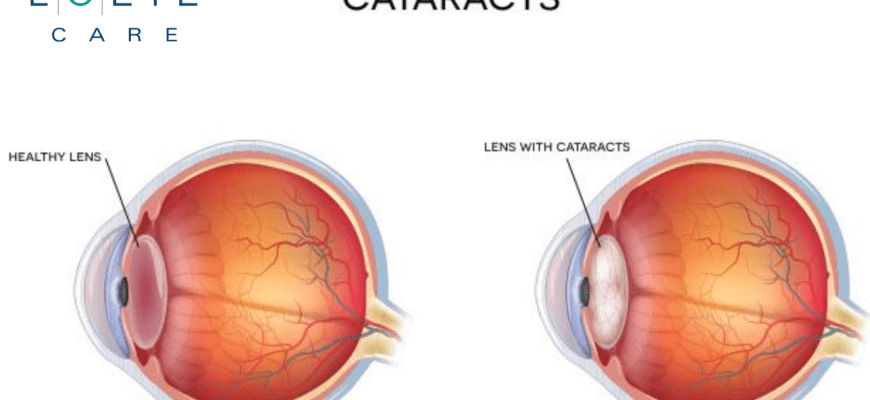
What Are Cataracts? Cataracts are a clouding of the eye’s natural lens that affects vision. They develop slowly and are most common in
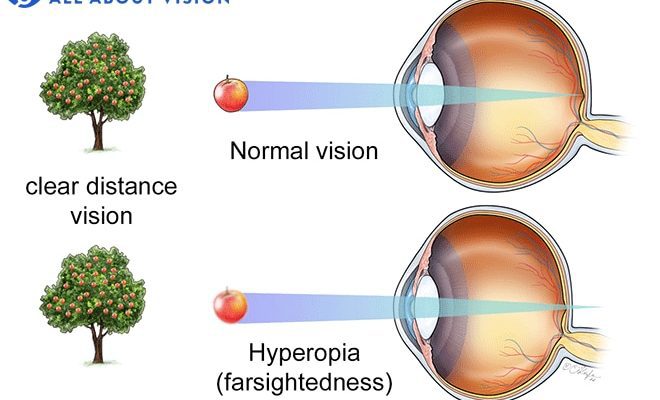
What is Farsightedness? Farsightedness (hyperopia) is a common refractive error where distant objects appear clearer than nearby objects.