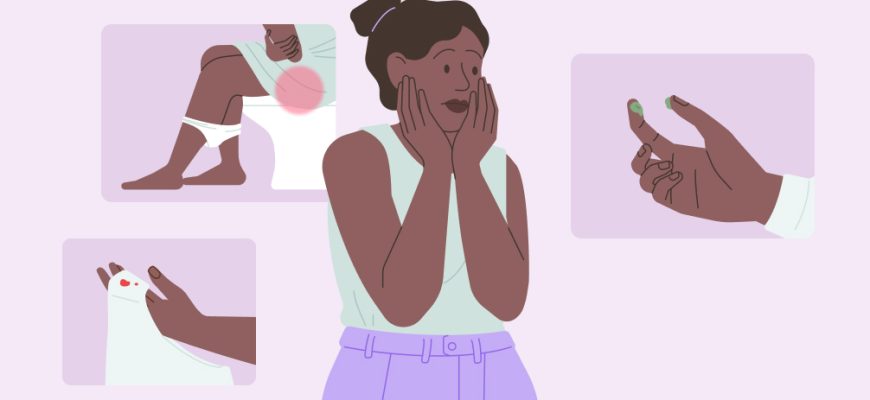
Venereology
About Health
1. Etiology 2. Transmission High-risk groups: 3. Symptoms 4. Diagnosis 5. Prevention 6. Treatment Medications: Additional steps: 7. How to Recognize?
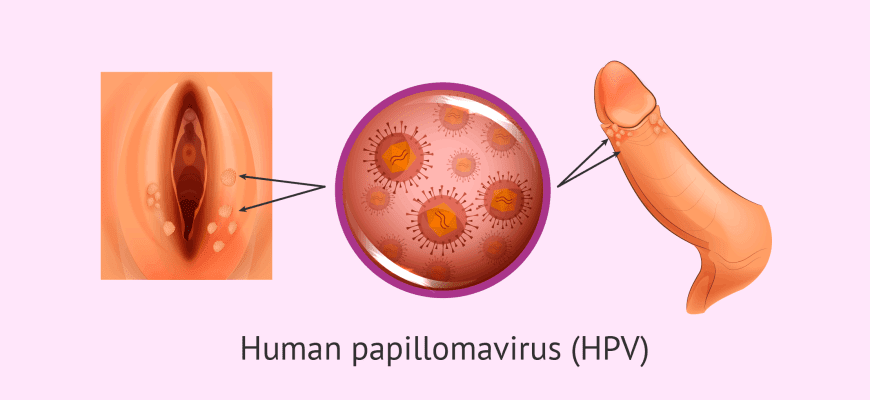
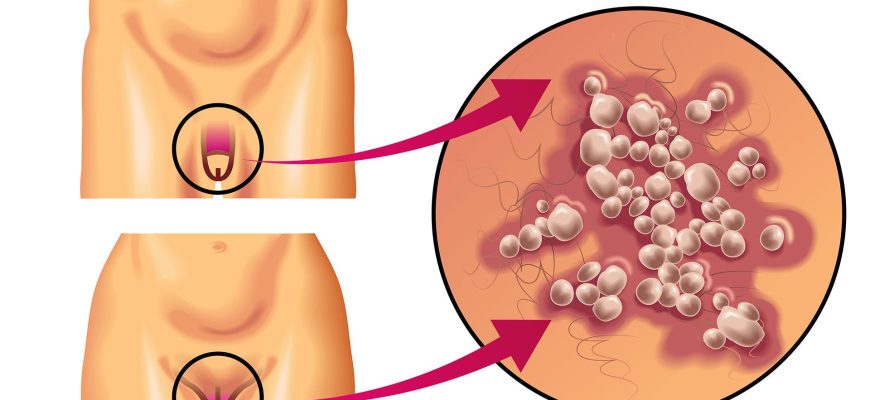
1. Etiology 2. Transmission Risk factors: 3. Symptoms By HPV type: Note: 90% of cases show no symptoms! 4. Diagnosis 5. Prevention 6.
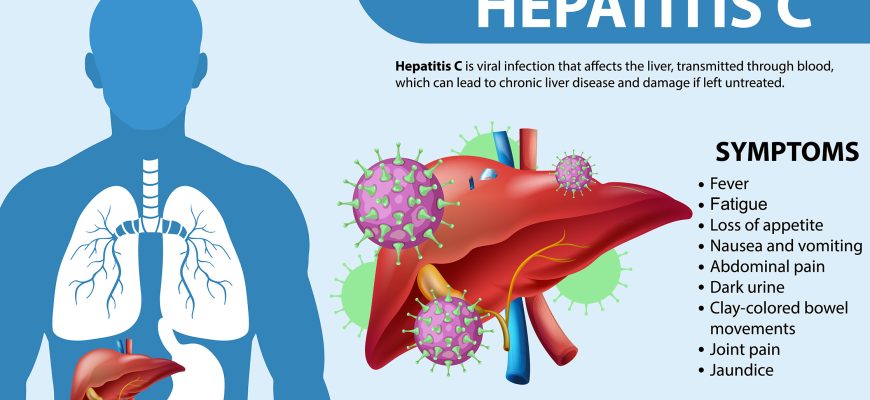
1. Etiology 2. Transmission Not transmitted: 3. Symptoms Acute phase (first 6 months): Chronic form: 4. Diagnosis Key point: 5. Prevention 6.
1. Etiology 2. Transmission 3. Symptoms Primary infection: Recurrences (milder): 4. Diagnosis Note: 5. Prevention 6. Treatment Acute phase: Suppressive
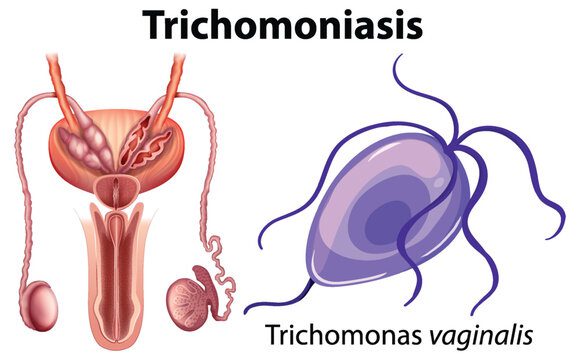
1. Etiology 2. Transmission 3. Symptoms In women (70% symptomatic): In men (50% asymptomatic): 4. Diagnosis Key point: Test both partners!
1. Etiology Pathogens: 2. Transmission 3. Symptoms In men: In women: Special risks: 4. Diagnosis Diagnostic criteria: 5. Prevention 6. Treatment Protocols: Key notes: 7.
1. Etiology Pathogen: Chlamydia trachomatis (obligate intracellular bacterium). 18 known serovars: 2. Transmission Routes 3. Symptoms In men: In women
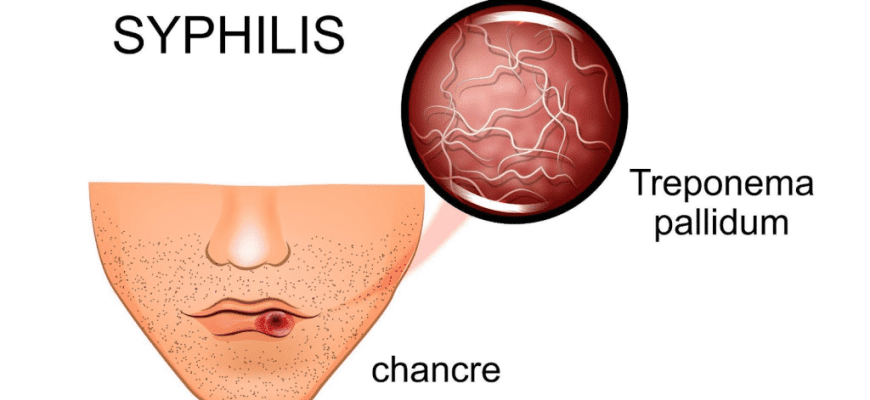
1. Etiology Pathogen: Treponema pallidum, a spiral-shaped bacterium from the spirochete family. Highly mobile, poorly stained by conventional methods (hence “
Gonorrhea (the clap) is a bacterial infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It affects the mucous membranes of the genitals, rectum, throat, and eyes.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), are infections primarily spread through sexual contact (vaginal, anal, oral).