Contents
1. Etiology
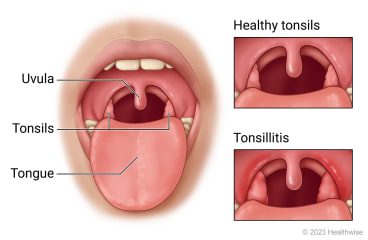
Tonsillitis – inflammation of palatine tonsils, most commonly caused by:
- Viruses (70-80% cases):
- Adenoviruses
- Rhinoviruses
- Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis)
- Bacteria (15-30%):
- Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (GAS) – most dangerous
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Less common: pneumococci, H. influenzae
2. Symptoms
Common manifestations:
- Severe sore throat worsening with swallowing
- Enlarged and reddened tonsils
- White or yellow coating/pus on tonsils
- Swollen cervical lymph nodes
Additional symptoms:
- Fever (up to 39-40°C in bacterial form)
- Headache, weakness
- Hoarseness (if larynx involved)
Chronic tonsillitis:
- Periodic exacerbations (2-3 times yearly)
- Bad breath
- Low-grade fever (37-37.5°C)
3. Diagnosis
- ENT examination:
- Pharyngoscopy (tonsil assessment)
- Lab tests:
- CBC (leukocytosis in bacterial infection)
- Rapid strep test
- Throat culture
- Additional:
- ASO (antistreptolysin-O) if streptococcal infection suspected
4. Treatment
Viral tonsillitis:
- Warm fluids
- Gargling (chamomile, furacilin)
- Antipyretics (paracetamol, ibuprofen)
Bacterial tonsillitis:
- Antibiotics (10-day course):
- Penicillins (amoxicillin) – first-line
- Macrolides (azithromycin) if penicillin allergy
- Local antiseptics (Hexoral, Tantum Verde)
Surgical treatment (chronic cases):
- Tonsillectomy
5. Prevention
- Oral hygiene
- Immune support (hardening, vitamins)
- Timely dental/nasal disease treatment
- Avoiding hypothermia
6. When to See a Doctor?
- Sore throat >3 days
- Fever >38.5°C
- Breathing/swallowing difficulty
- Rash appearance
- Dehydration signs
7. How to Prevent Tonsillitis?
- Regular handwashing
- Avoid sick contacts
- Don’t share utensils
- Maintain home air humidity
When to Remove Tonsils?
✅ Indications for Tonsillectomy
- Recurrent infections:
- 7+ sore throats/year
- 5+/year for 2 years
- 3+/year for 3 years
- Complications:
- Peritonsillar abscess
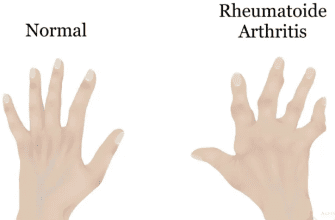
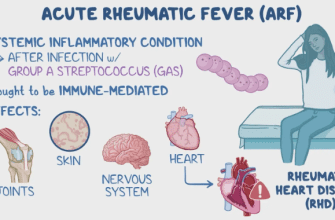
- Rheumatic fever
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
- Other:
- Sleep apnea (enlarged tonsils)
- Chronic bad breath
- Suspected cancer
❌ When to Keep Tonsils?
- Viral infections (rare episodes).
- No systemic complications.
- Good response to conservative treatment (washing, physiotherapy).
Note:
- Children <5-6 years: tonsils are important for immunity.
- Adults >40: surgery is riskier.
Alternatives:
- Laser ablation
- Cryotherapy