What is this?
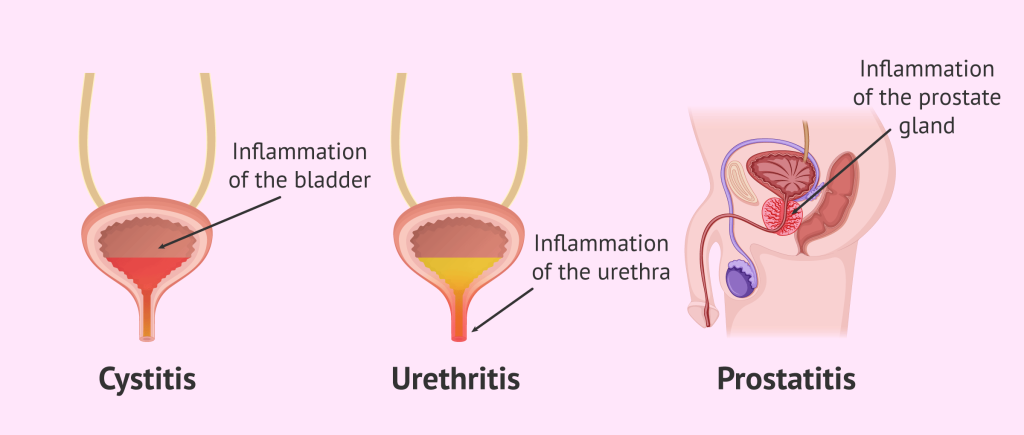
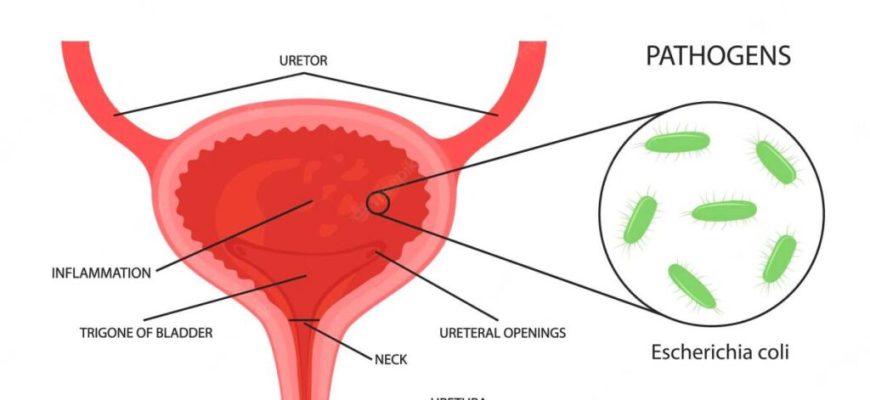
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder, usually caused by a bladder infection. It’s a common type of urinary tract infection (UTI),
Causes
- bacteria in the urinary tract – E.coli, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- using a diaphragm for contraception
- inserting a tampon or urinary catheter (a thin tube inserted into the urethra to drain the bladder)
- sex
Symptoms
Symptoms of cystitis include:
- pain, burning or stinging when you pee
- needing to pee more often and urgently than usual
- pee that’s dark, cloudy or strong smelling
- pain low down in your tummy
Symptoms in young children may also include:
- a high temperature – they feel hotter than usual if you touch their neck, back or tummy
- wetting themselves
- reduced appetite and being sick
- weakness and irritability
In older, frail people with cognitive impairment (such as dementia) and people with a urinary catheter, symptoms may also include:
- changes in behaviour, such as acting confused or agitated (delirium)
- wetting themselves more than usual
- shivering or shaking
Treatment
- a course of antibiotics:
-Nitrofurantoin 100 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (SMX-TMP) double-strength twice a day for three days (if local antibiotic resistance is <20%)
-Fosfomycin 3 gm as a single oral dose - take paracetamol or ibuprofen
- drink plenty of water
- hold a hot water bottle over your lower tummy
- avoid having sex
- avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder, like fruit juices, coffee and alcohol
- pee frequently
Prevention
- go to the toilet whenever you want and empty your bladder completely
- maintain hygiene – empty your bladder immediately after sex
- wipe your genitals from front to back
- wear cotton underwear, no synthetics
- do not use scented shower gels or soaps in the genital area. use the most common, unscented ones
- take showers rather than baths more often. Exposing the genitals to chemicals for too long while taking a bath