Contents
1. Etiology
Otitis – ear inflammation classified by location:
A. External otitis (ear canal):
- Bacteria (Pseudomonas, S. aureus)
- Fungi (Candida) – after prolonged antibiotic use
- Allergy (to cosmetics, earbuds)
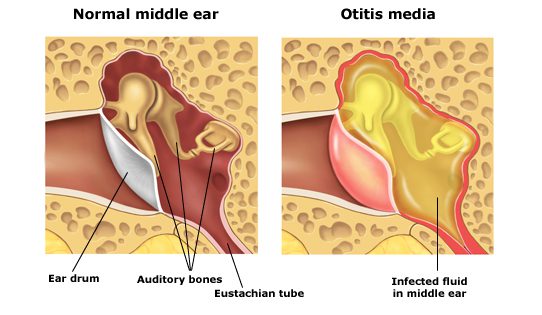
B. Middle ear otitis:
- Viruses (rhinoviruses) – 60% cases
- Bacteria (S. pneumoniae) – 30%
C. Labyrinthitis – rare complication.
2. Symptoms
External otitis:
- Pain when pressing tragus
- Itching, swollen ear canal
- Purulent discharge
Acute middle otitis:
- Ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Fever (in children)
- Otorrhea (if perforated)
Chronic otitis:
- Persistent discharge
- Progressive hearing loss
Labyrinthitis:
- Vertigo, nausea
- Tinnitus
3. Diagnosis
- Otoscopy:
- Redness in external otitis
- Bulging/perforated eardrum
- Tympanometry
- Audiometry (chronic cases)
- Lab tests:
- CBC (leukocytosis)
- Culture (if pus present)
4. Treatment
External otitis:
- Antibiotic drops (Ciprofloxacin)
- Antifungal creams (Clotrimazole)
Middle otitis:
- Antibiotics (Amoxicillin)
- Nasal decongestants
- Myringotomy (if pus accumulation)
Labyrinthitis:
- IV antibiotics
- Vestibular suppressants
5. Prevention
- Proper nose-blowing technique
- Use swimming earplugs
- Treat URIs promptly
- Avoid cotton swabs
6. Red Flags
- Pain >48 hours
- Fever >38°C
- Purulent discharge
- Hearing loss/vertigo
- Symptoms in infants
7. Prevention Tips
- Vaccination (PCV, flu vaccine)
- Breastfeeding (for infants)
- Allergy management
8.When to See a Doctor?
- Vertigo
- Pus discharge
- Symptoms in infants
- Severe pain + fever
Warning: Never use ear drops without prescription if eardrum is perforated!