Contents
1. Etiology (Causes)
Acromegaly is caused by excessive growth hormone (GH) production, typically from:
- Pituitary adenoma (benign tumor) – 95% of cases
- Ectopic GH secretion (rare, from lung/pancreatic tumors)
- Genetic syndromes (MEN-1, Carney complex)
Key Mechanism: GH overproduction → Increased IGF-1 → Abnormal tissue growth
2. Symptoms
Early Signs (Often Overlooked):
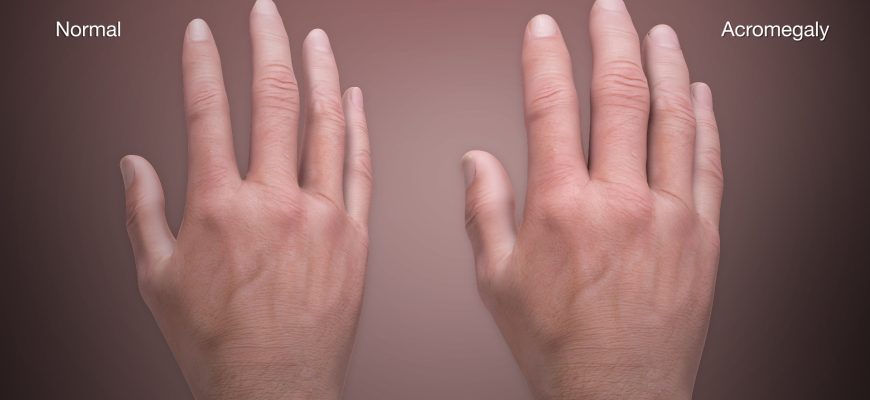
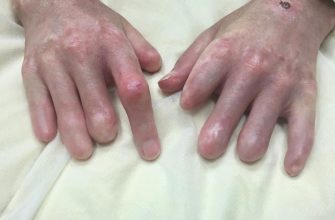
- Gradual enlargement of hands/feet (ring/watch no longer fits)
- Coarsening facial features (prominent brow/nose, jaw protrusion)
- Increased shoe/hat size
Advanced Symptoms:
- Physical Changes:
- Thickened skin/oily complexion
- Macroglossia (enlarged tongue)
- Widened tooth spacing
- Systemic Effects:
- Joint pain/arthritis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Hypertension (50% of patients)
- Sleep apnea (60% of cases)
- Glucose intolerance (25-45%)
3. Diagnosis
Diagnostic Triad:
- IGF-1 blood test (elevated)
- Oral glucose tolerance test (GH fails to suppress)
- Pituitary MRI (identifies adenoma size/location)
Additional Tests:
- Visual field testing (for tumor compression)
- Colonoscopy (increased cancer risk)
- Echocardiogram (cardiomegaly screening)
4. Treatment
First-Line Options:
- Transsphenoidal surgery (cures 80% of microadenomas)
- Medical Therapy:
- Somatostatin analogs (octreotide/lanreotide)
- GH receptor antagonists (pegvisomant)
- Dopamine agonists (cabergoline)
Radiation Therapy (if surgery/meds fail):
- Gamma knife radiosurgery
- Conventional radiation
5. Prevention
No Primary Prevention, but early detection helps:
- Monitor if you have:
- Family history of pituitary tumors
- MEN-1 syndrome
- Unexplained growth changes
6. When to See a Doctor?
Seek evaluation for:
- Progressive enlargement of extremities
- New-onset sleep apnea/snoring
- Unexplained hypertension/diabetes
- Change in facial appearance over years
- Ring/watch no longer fitting
7. Disease Management
Critical Monitoring:
- Annual:
- IGF-1 levels
- Pituitary MRI (if residual tumor)
- Colonoscopy (every 3-5 years)
- Cardiac echo
Key Statistics:
- Diagnosis delay: Average 7-10 years
- Mortality: 2-3x higher if untreated
- Surgical cure rates:
- Microadenomas: 80-90%
- Macroadenomas: 40-60%
Visual Diagnosis Clues
Characteristic Facial Features:
- Prominent supraorbital ridge
- Thickened nasal cartilage
- Prognathism (jaw protrusion)
- Deepened skin folds
Hand Findings:
- Spade-like appearance
- Thickened fingers
- Positive “ring sign” (can’t remove wedding ring)