Contents
1. Etiology (Causes)
Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by:
- Autoimmune disorders:
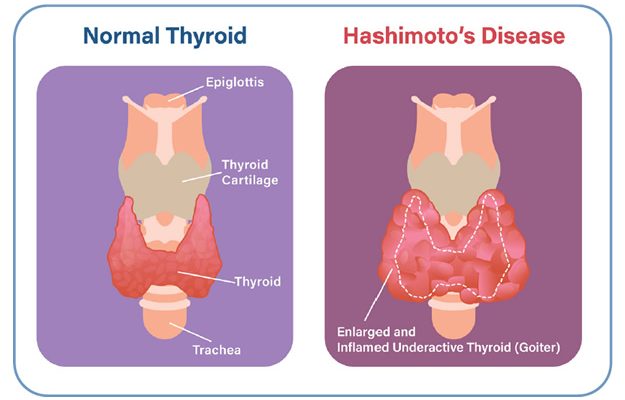
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (most common, leads to hypothyroidism).
- Postpartum thyroiditis (occurs after childbirth).
- Viral infections (subacute thyroiditis, e.g., after a cold).
- Bacterial/fungal infections (rare, seen in immunocompromised patients).
- Radiation exposure (after treatment for hyperthyroidism or cancer).
- Medications (lithium, amiodarone, interferon).
2. Symptoms
Symptoms vary by type:
| Type of Thyroiditis | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Hashimoto’s | Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, hair loss. |
| Subacute (De Quervain’s) | Painful thyroid, fever, fatigue, hyperthyroidism (early) → hypothyroidism (later). |
| Postpartum | Hyperthyroidism (anxiety, weight loss) → hypothyroidism (fatigue, depression). |
| Acute (infectious) | Severe neck pain, fever, difficulty swallowing. |
3. Diagnosis
- Blood tests:
- TSH, T3, T4 (high/low depending on phase).
- Thyroid antibodies (anti-TPO in Hashimoto’s).
- ESR/CRP (elevated in subacute thyroiditis).
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound (enlarged thyroid, reduced blood flow in Hashimoto’s).
- Radioactive iodine uptake scan (low in subacute, high in Graves’).
- Fine-needle biopsy (if infection or cancer is suspected).
4. Treatment
- Hashimoto’s → Levothyroxine (lifelong for hypothyroidism).
- Subacute → NSAIDs (ibuprofen) or steroids for pain/inflammation.
- Postpartum → Usually resolves on its own; may need temporary thyroid hormones.
- Acute (infectious) → Antibiotics (if bacterial) + drainage if abscess forms.
5. Prevention
- No guaranteed prevention, but reduce risk by:
- Avoiding excessive iodine intake.
- Managing autoimmune conditions (e.g., diabetes, celiac disease).
- Monitoring thyroid function after pregnancy or radiation exposure.
6. When to See a Doctor?
- Persistent fatigue, weight changes, or mood swings.
- Painful/swollen thyroid (especially with fever).
- Postpartum symptoms (anxiety, heart palpitations, depression).
- Family history of autoimmune thyroid disease.
7. How to Avoid Thyroiditis?
- Limit radiation exposure (when possible).
- Check thyroid levels if taking lithium/amiodarone.
- Vaccinations (reduce viral triggers).
- Healthy diet (selenium, zinc support thyroid function).
Key Takeaways
- Hashimoto’s = Autoimmune → Hypothyroidism.
- Subacute = Viral → Painful, transient hyper/hypo.
- Postpartum = Temporary thyroid dysfunction.
- Acute = Infection → Medical emergency.
Early diagnosis prevents complications (e.g., heart disease, infertility). If you suspect thyroiditis, get tested (TSH + antibodies).