What is this?
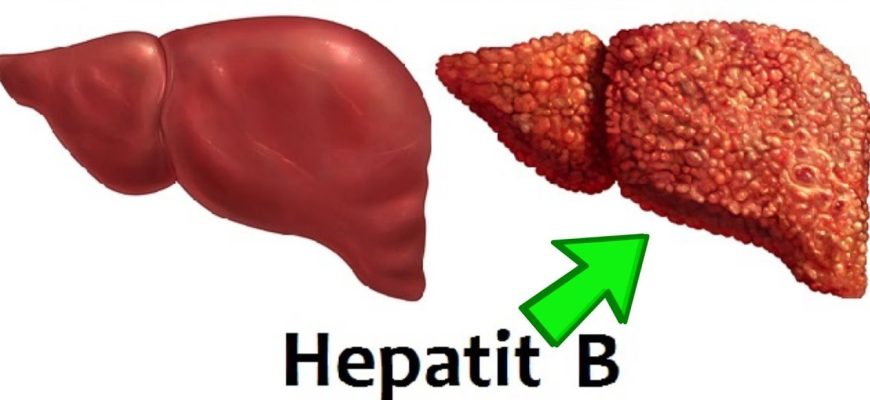
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that primarily affects the liver. It can range from an acute, self-limiting illness to a chronic, lifelong condition that may lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Causes
- Transmission occurs through contact with infectious body fluids, including:
- Blood.
- Semen.
- Vaginal secretions.
- Saliva (less common).
Risk Factors
- Unprotected Sex: Multiple sexual partners or unprotected intercourse.
- Needle Sharing: Intravenous drug use with contaminated needles.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission: During childbirth (vertical transmission).
- Healthcare Exposure: Needlestick injuries or inadequate sterilization of medical equipment.
- Blood Transfusions: In regions with inadequate blood screening.
- Living in Endemic Areas: High prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa, East Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
- Household Contact: Sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes with an infected person.
- Immunocompromised States: HIV infection or immunosuppressive therapy.
Types of Hepatitis B
Acute Hepatitis B:
- Short-term infection (less than 6 months).
- Most adults recover completely.
- Symptoms may range from mild to severe.
Chronic Hepatitis B:
- Long-term infection (more than 6 months).
- More common in infants and children (90% risk if infected at birth).
- Can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Symptoms
Acute Hepatitis B:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes).
- Dark urine and pale stools.
- Abdominal pain (especially in the liver area).
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
- Fever and joint pain.
Chronic Hepatitis B:
- Often asymptomatic for years.
- Symptoms may appear only after significant liver damage:
- Jaundice.
- Swelling in the abdomen (ascites).
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Confusion or hepatic encephalopathy.
Diagnosis
Blood Tests:
- HBsAg (Hepatitis B Surface Antigen): Indicates active infection (acute or chronic).
- Anti-HBs (Hepatitis B Surface Antibody): Indicates recovery or immunity (from vaccination).
- Anti-HBc (Hepatitis B Core Antibody): Indicates past or current infection.
- HBV DNA: Measures viral load and activity.
- Liver function tests (elevated ALT and AST).
Imaging:
- Ultrasound to assess liver damage or complications.
Liver Biopsy:
- To evaluate the extent of liver inflammation or fibrosis.
Treatment
Acute Hepatitis B:
- Usually self-limiting; supportive care is the mainstay:
- Rest.
- Adequate hydration.
- Avoidance of alcohol and hepatotoxic drugs.
Chronic Hepatitis B:
- Antiviral Medications:
- Tenofovir or entecavir (first-line treatments to suppress viral replication).
- Interferon Therapy:
- Pegylated interferon-alpha (boosts immune response; used in select cases).
- Regular Monitoring:
- Liver function tests and viral load monitoring.
- Liver Transplant:
- For end-stage liver disease or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Complications
Chronic Liver Disease:
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver).
- Liver failure.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
- Primary liver cancer.
Fulminant Hepatitis:
- Rare, life-threatening acute liver failure.
Extrahepatic Manifestations:
- Kidney disease (membranous nephropathy).
- Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels).
Prevention
Vaccination:
- Hepatitis B vaccine (3-dose series: 0, 1, and 6 months).
- Recommended for all infants, healthcare workers, and high-risk individuals.
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis:
- Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and vaccine for unvaccinated individuals exposed to HBV.
Safe Practices:
- Use of condoms during sex.
- Avoid sharing needles or personal items like razors.
- Proper sterilization of medical equipment.
Screening and Education:
- Routine screening for pregnant women and high-risk populations.
- Public awareness campaigns about transmission and prevention.
Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission:
- Administer HBIG and vaccine to newborns of HBV-positive mothers.