1. Etiology
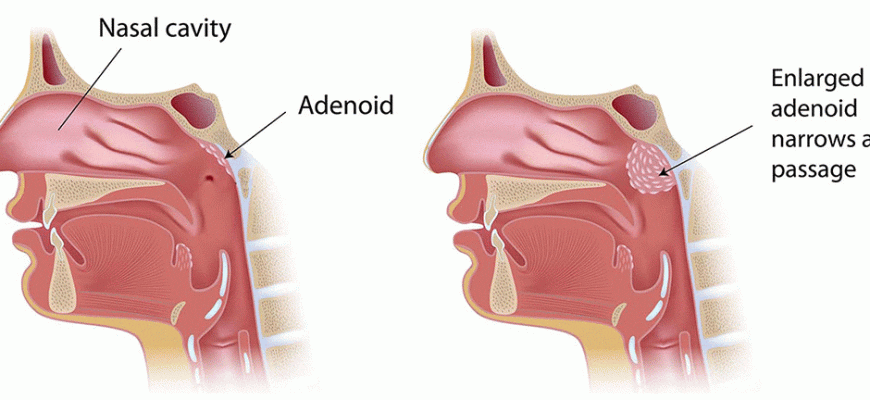
Adenoids (pharyngeal tonsil) – lymphoid tissue of the immune system. Problems occur when hypertrophied:
- Physiological growth (peak activity 3-7 years)
- Recurrent infections (URIs, strep throat)
- Allergies (chronic rhinitis)
- Genetic predisposition
2. Symptoms
Main signs:
- Chronic nasal obstruction (mouth breathing)
- Snoring and sleep apnea
- Hyponasal speech
- Recurrent otitis and sinusitis
- Adenoid facies (long-term):
- Open mouth
- Elongated face
- Malocclusion
Associated:
- Hearing loss
- Morning cough
- Fatigue
3. Diagnosis
- Anterior rhinoscopy
- Posterior rhinoscopy (mirror)
- Nasopharyngoscopy (gold standard)
- X-ray/CT (for complications)
- Audiometry (if hearing loss)
4. Treatment
Conservative (grade I-II):
- Nasal steroids (Mometasone 1-3 months)
- Saline irrigation
- Lymphotropic drugs
- Physiotherapy (laser, UV)
Surgical (adenoidectomy) indications:
- Grade III hypertrophy
- 4 ear infections/year
- Sleep apnea
- Facial skeleton deformation
5. Prevention
- Prompt URI treatment
- Chronic infection control
- Allergy management
- Hardening procedures
- Vaccination (PCV, influenza)
6. Red Flags
- Mouth breathing >1 month
- Snoring with breath pauses
- Frequent colds (>6/year)
- Recurrent otitis
- Hearing impairment
7. Prevention Tips
- Teach proper nose-blowing
- Avoid secondhand smoke
- Maintain 50-60% humidity
- Limit contact with sick people
- Timely dental care