A heart-healthy diet is critical for managing and preventing conditions like hypertension, coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, and stroke. Proper nutrition helps control blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation while supporting overall heart function.
- Key Dietary Goals for CVD
- Recommended Foods for Heart Health
- 1. Heart-Healthy Fats
- 2. High-Fiber Foods
- 3. Lean Proteins
- 4. Fruits & Vegetables (Rich in Antioxidants & Potassium)
- 5. Low-Fat Dairy (or Dairy Alternatives)
- Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Dietary Approaches for Specific CVD Conditions
- 1. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- 2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) / High Cholesterol
- 3. Heart Failure
- 4. Atherosclerosis (Plaque Buildup)
- Key Supplements for Heart Health
- Lifestyle Tips for CVD Management
- When to See a Dietitian?
- Prognosis
Key Dietary Goals for CVD
✔ Lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol
✔ Reduce blood pressure
✔ Control blood sugar (prevent diabetes-related CVD)
✔ Maintain healthy weight
✔ Decrease inflammation
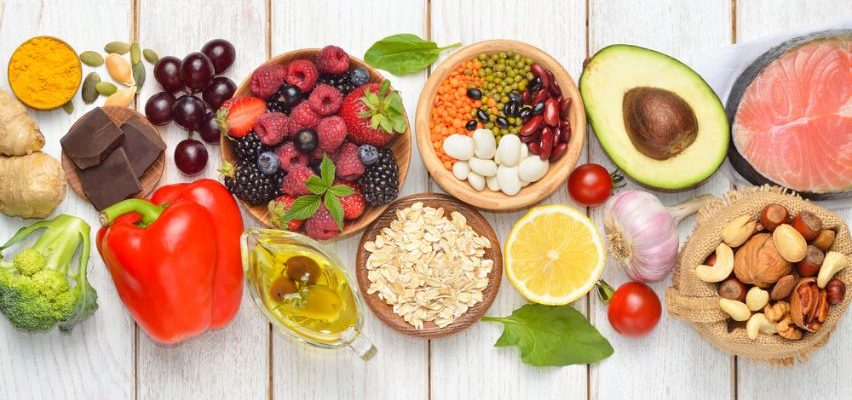
Recommended Foods for Heart Health
1. Heart-Healthy Fats
- Monounsaturated fats (MUFAs): Olive oil, avocados, nuts (almonds, cashews)
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, walnuts
- Plant sterols/stanols: Fortified margarines, nuts (help block cholesterol absorption)
2. High-Fiber Foods
- Soluble fiber: Oats, beans, lentils, apples (lowers LDL cholesterol)
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread (avoid refined grains)
3. Lean Proteins
- Fish & poultry: Skinless chicken, turkey, cod
- Plant-based proteins: Tofu, tempeh, legumes (reduce saturated fat intake)
4. Fruits & Vegetables (Rich in Antioxidants & Potassium)
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale (high in nitrates for blood pressure)
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries (reduce oxidative stress)
- Potassium-rich foods: Bananas, sweet potatoes, tomatoes (counteract sodium effects)
5. Low-Fat Dairy (or Dairy Alternatives)
- Skim milk, Greek yogurt, fortified almond/soy milk (calcium + vitamin D)
Foods to Limit or Avoid
❌ Trans fats & hydrogenated oils (fried foods, packaged snacks)
❌ Excess saturated fats (fatty meats, butter, full-fat dairy)
❌ High-sodium foods (processed meats, canned soups, fast food)
❌ Added sugars (sodas, pastries, sweetened cereals)
❌ Excess alcohol (≤1 drink/day for women, ≤2 for men)
Dietary Approaches for Specific CVD Conditions
1. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension):
- High in fruits, veggies, low-fat dairy
- Low in sodium (<1,500–2,300 mg/day)
- Includes nuts, seeds, whole grains
2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) / High Cholesterol
- Mediterranean Diet:
- Olive oil as primary fat
- Fatty fish ≥2x/week
- Minimal red meat, processed foods
3. Heart Failure
- Fluid & sodium restriction (if edema present)
- Small, frequent meals (eases digestion)
- High-protein, nutrient-dense foods (prevent muscle wasting)
4. Atherosclerosis (Plaque Buildup)
- Focus on anti-inflammatory foods: Turmeric, garlic, green tea
- Avoid refined carbs & sugary drinks (reduce triglycerides)
Key Supplements for Heart Health
- Omega-3 fish oil (1,000 mg/day EPA+DHA – lowers triglycerides)
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) (may help with statin-related muscle pain)
- Magnesium (supports blood pressure regulation)
- Plant sterols (2g/day – lowers LDL cholesterol)
Note: Always consult a doctor before starting supplements, especially if on blood thinners (e.g., warfarin).
Lifestyle Tips for CVD Management
- Limit salt (use herbs/spices instead)
- Cook at home (control ingredients)
- Read labels (watch for hidden sodium/sugar)
- Stay hydrated (water > sugary drinks)
- Combine diet with exercise (30+ mins daily)
When to See a Dietitian?
- Recent heart attack or stent placement
- Struggling with cholesterol/blood pressure control
- Need for personalized meal plans (e.g., diabetes + CVD)
Prognosis
- Diet changes can reduce CVD risk by 30% (American Heart Association).
- Mediterranean/DASH diets lower heart attack & stroke risk.
- Lifestyle + medication = best outcomes for severe CVD.