Thrush, also called vaginal yeast infection, is a fungal infection caused by Candida species (most commonly Candida albicans). It leads to inflammation, itching, and thick white discharge.
- Causes
- Risk Factors
- Types of Thrush (Candidiasis)
- 1. Oropharyngeal Thrush (Oral Yeast Infection)
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- 2. Vaginal Thrush (Vaginal Candidiasis)
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- 3. Male Genital Thrush (Candidal Balanitis)
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- 4. Esophageal Thrush (Candida Esophagitis)
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- 5. Cutaneous (Skin) Thrush
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- 6. Invasive Candidiasis (Systemic Infection)
- Symptoms:
- Causes/Risk Factors:
- Treatment:
- Key Differences Between Types
- Prevention Tips for All Types
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- 1. Antifungal Medications
- 2. Home Remedies (Supportive Care)
- 3. Treatment for Recurrent Thrush (≥4 episodes/year)
- Complications
- Prevention
- Prognosis
Causes
- Fungal Overgrowth: Candida is normally present in the vagina but overgrows when the balance of bacteria and yeast is disrupted.
- Contributing Factors:
- Antibiotics (kill protective bacteria, allowing yeast to thrive)
- High estrogen levels (pregnancy, birth control pills)
- Uncontrolled diabetes (high sugar promotes yeast growth)
- Weakened immune system (HIV, steroids, chemotherapy)
- Tight, non-breathable clothing (creates a moist environment)
- Sexual activity (can introduce or spread yeast, though not an STI)
Risk Factors
- Recent antibiotic use
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes (especially poorly controlled)
- Immunosuppression (HIV, corticosteroids)
- Hormonal contraceptives or hormone therapy
- Frequent douching or use of scented products
Types of Thrush (Candidiasis)
Thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans. It can affect different parts of the body, leading to various forms of thrush. Below are the main types:
1. Oropharyngeal Thrush (Oral Yeast Infection)
Affected Area: Mouth, tongue, throat.
Common in: Infants, elderly, immunocompromised individuals.
Symptoms:
- White, creamy patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or throat
- Redness, soreness, or bleeding when scraped
- Difficulty swallowing (if severe)
- Loss of taste
Causes/Risk Factors:
- Weakened immune system (HIV, chemotherapy)
- Antibiotic or steroid use
- Diabetes (poorly controlled)
- Dentures (poorly fitted or unclean)
- Smoking
Treatment:
- Antifungal mouthwash (nystatin)
- Lozenges (clotrimazole)
- Oral fluconazole (for severe cases)
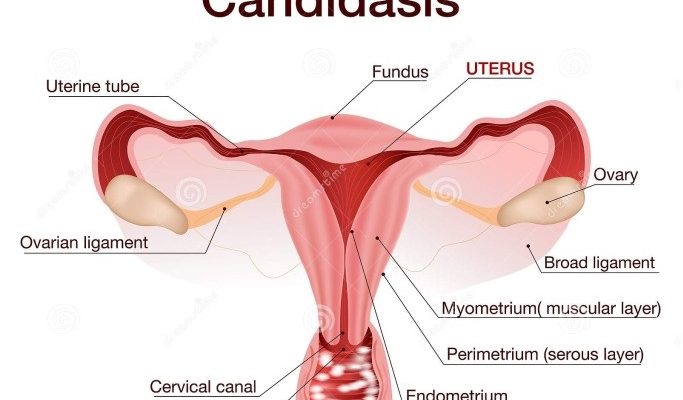
2. Vaginal Thrush (Vaginal Candidiasis)
Affected Area: Vagina, vulva.
Common in: Women of reproductive age.
Symptoms:
- Thick, white, “cottage cheese-like” discharge
- Intense itching, redness, swelling
- Burning during urination or sex
Causes/Risk Factors:
- Antibiotics, hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control)
- Diabetes, weakened immunity
- Tight clothing, poor hygiene
Treatment:
- Antifungal creams/suppositories (clotrimazole, miconazole)
- Oral fluconazole (single dose)
3. Male Genital Thrush (Candidal Balanitis)
Affected Area: Penis (glans, foreskin).
Common in: Uncircumcised men, diabetics.
Symptoms:
- Red, itchy rash on the penis
- White, clumpy discharge under the foreskin
- Burning during urination or sex
Causes/Risk Factors:
- Unprotected sex with a partner who has thrush
- Poor hygiene, diabetes
- Antibiotic use
Treatment:
- Topical antifungals (clotrimazole cream)
- Oral fluconazole (if severe)
4. Esophageal Thrush (Candida Esophagitis)
Affected Area: Esophagus (food pipe).
Common in: HIV/AIDS patients, chemotherapy recipients.
Symptoms:
- Painful swallowing
- Chest pain (behind the breastbone)
- Nausea, vomiting (white patches)
Causes/Risk Factors:
- Severe immune suppression (HIV, cancer treatment)
- Untreated oral thrush spreading downward
Treatment:
- Oral fluconazole (first-line)
- IV antifungals (for severe cases, e.g., amphotericin B)
5. Cutaneous (Skin) Thrush
Affected Area: Skin folds (armpits, groin, under breasts).
Symptoms:
- Red, itchy, moist rash
- Satellite lesions (small patches near main rash)
Causes/Risk Factors:
- Obesity (skin folds trap moisture)
- Hot/humid climates
- Poor hygiene
Treatment:
- Topical antifungals (clotrimazole, miconazole powder)
- Keep area dry (use absorbent fabrics)
6. Invasive Candidiasis (Systemic Infection)
Affected Area: Blood, organs (kidneys, heart, brain).
Most serious type—requires urgent treatment.
Symptoms:
- High fever, chills
- Organ-specific symptoms (e.g., kidney failure, endocarditis)
Causes/Risk Factors:
- ICU patients (catheters, IV lines)
- Severe burns, major surgery
- Neutropenia (very low white blood cells)
Treatment:
- IV antifungals (e.g., caspofungin, fluconazole)
Key Differences Between Types
| Type | Location | High-Risk Groups | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Thrush | Mouth, throat | Babies, HIV+ | Nystatin swish |
| Vaginal Thrush | Vagina, vulva | Pregnant women | Clotrimazole cream |
| Male Thrush | Penis | Diabetic men | Antifungal cream |
| Esophageal Thrush | Esophagus | AIDS patients | Oral fluconazole |
| Skin Thrush | Skin folds | Obese individuals | Antifungal powder |
| Invasive Candidiasis | Blood, organs | ICU patients | IV antifungals |
Prevention Tips for All Types
✔ Maintain good hygiene (especially in moist areas)
✔ Avoid unnecessary antibiotics
✔ Control blood sugar (if diabetic)
✔ Wear breathable fabrics (cotton underwear)
✔ Use probiotics (yogurt, supplements)
Symptoms
- Intense vaginal itching
- Thick, white, “cottage cheese-like” discharge (odorless or slightly yeasty)
- Redness, swelling, and soreness of the vulva
- Burning during urination or sex
- Small cuts or fissures (due to skin irritation)
Diagnosis
- Medical history & symptom review
- Pelvic exam (checks for redness, swelling, discharge)
- Microscopic exam (KOH prep) – Reveals yeast hyphae or buds
- Vaginal pH test (normal in yeast infections: 3.8–4.5)
- Culture (if recurrent or resistant to treatment)
Treatment
1. Antifungal Medications
- Topical (vaginal creams/suppositories):
- Clotrimazole (1%, 2%, or 3-day treatments)
- Miconazole (Monistat)
- Oral medication:
- Fluconazole (Diflucan) – Single 150mg dose
2. Home Remedies (Supportive Care)
- Probiotics (Lactobacillus strains may help restore balance)
- Yogurt (plain, unsweetened) – Applied topically or eaten
- Avoid irritants (scented soaps, douches, tight underwear)
3. Treatment for Recurrent Thrush (≥4 episodes/year)
- Long-term antifungal therapy (e.g., fluconazole weekly for 6 months)
- Address underlying causes (e.g., better diabetes control)
Complications
- Chronic/recurrent infections
- Secondary bacterial infections (from scratching)
- Vulvar skin breakdown (fissures, ulcers)
- Sexual dysfunction (due to pain during intercourse)
Prevention
- Wear cotton underwear & loose clothing
- Avoid douching & scented hygiene products
- Change out of wet swimwear/sweaty clothes quickly
- Limit sugar & refined carbs (yeast thrives on sugar)
- Probiotic-rich foods (yogurt, kefir, fermented foods)
- Good diabetes control (if applicable)
Prognosis
- Most cases resolve within days with proper treatment.
- Recurrence is common (30–50% of women experience repeat episodes).
- Chronic cases may require long-term antifungal therapy.